2013年11月4日NetFuel, Inc. (以下稱NetFuel),於美國伊利諾北區聯邦地方法院東分院(United States District Court, The Northern District of Illinois, Eastern Division)向F5 Networks, Inc.(以下稱F5)提起專利侵權訴訟,指控F5所提供的多款軟體侵害Netfuel所擁有的US7,747,730 (以下簡稱’730專利)與US8,131,851 (以下簡稱’851專利)兩篇美國專利。
NetFuel創建於1999年,以建立金融服務業的交易系統起家,目前該公司主要業務為提供金融機構各種金融與交易操作系統解決方案、硬體平台等基礎架構設施支援服務。NetFuel所開發之軟體技術目前取得兩項美國專利,即為本案兩項系爭專利。本案兩項系爭專利名稱皆為「電腦網路資源管理(Managing computer network resources)」,可提供具有擴展性與高效運行的網路資源管理技術,使電腦網路系統運行能力,不受網路系統中工作節點數量,以及故障節點出現之影響。
F5 Networks創立於1996年是應用傳輸網路(Application Delivery Networking,ADN)與網路安全業者,主要業務為提供企業用戶各種建構AND之解決方案,以進行企業管理應用程式、伺服器、儲存設備與網路設備資源。
NetFuel控訴F5販售的BIG-IP系列套裝軟體,包括BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM)、BIG-IP Global Traffic Manager (GTM)、BIG-IP Access Policy Manager (APM)、BIG-IP Advanced Firewall Manager (AFM)、BIG-IP Application Acceleration Manager (AAM)、BIG-IP Application Security Manager (ASM)、BIG-IP Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) 、BIG-IP Edge Gateway、Enterprise Manager、BIG-IP Link Controller以及BIG-IP Policy Enforcement Manager (PEM)等產品,皆是利用了系爭兩項專利技術,F5未經NetFuel同意,即開發、製造、使用、銷售與提供販售該系列產品,已直接侵害NetFuel的專利權,包括’730專利第7-22、24、26-34項權利範圍,以及’851專利第8-17項權利範圍。NetFuel請求法院核發禁制令,以排除F5之侵權行為,並要求F5支付專利侵害損害賠償與訴訟相關費用。(796字;圖3)
表一、系爭專利為美國專利編號US7,747,730、US8,131,851
| 專利名稱 |
Managing computer network resources |
Managing computer network resources |
| 公開號 |
US7,747,730 |
US8,131,851 |
| 出版類型 |
授權 |
授權 |
| 申請書編號 |
10/186,526 |
12/789,450 |
| 發佈日期 |
2010年6月29日 |
2012年3月06日 |
| 申請日期 |
2002年6月28日 |
2010年5月27日 |
| 優先權日期 |
無 |
無 |
| 其他專利公開號 |
無 |
無 |
| 發明人 |
Harlow; James D. |
Harlow; James D |
| 原專利權人 |
Netfuel, Inc. |
Netfuel Inc |
| 圖示 |
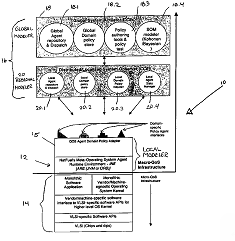 |
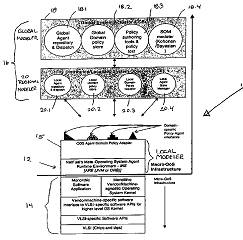 |
Source: 科技政策研究與資訊中心 — 科技產業資訊室整理,2013/11
表二、請求項解析
| US7,747,730請求項1 |
|
1. A method of managing a computer network, comprising: assigning a goal to a software, wherein the software agent has its own runtime environment; is able to communicate with other software agents in the computer network; is capable of perceiving its own state; and is able to clone itself, and wherein the goal is a programmatic expression of a predefined task for the software agent; and monitoring the computer network; creating test policy and modeling a behavior of the computer network based on the test policy to determine an optimal policy for the computer network, including predicting a failure of a network component based on a prediction algorithm; wherein said modeling comprises determining appropriate policy based on the prediction; and dynamically modifying the assigned goal of the software agent by replacing the assigned goal based on the optimal policy; wherein the software agent comprises an autonomous agent operable to request further policy when it lacks an ability to perform the predefined task.
|
1.一種電腦網路管理方法,包括:指派一目標給一軟體,該軟體代理人具有自有之執行環境、可與位於該電腦網路內的其他軟體代理人通訊、可查知自我狀態及可自行複製;該目標則為給予該軟體代理人之預先定義任務之程式化敘述;監控該電腦網路;產生測試指令,並根據該測試指令建模該電腦網路之行為,以決定一個對該電腦網路之最佳化指令,包括以一預測演算法預測一網路組件之錯誤;該建模行為包括基於該預測決定適當的指令;並基於該最佳指令,以置換該交付目標之方式動態修正交付該軟體代理人之目標;該軟體代理人包括一自動代理人,當其缺乏執行該被預訂任務之能力時,可要求更多指令。
|
| US8,131,851請求項1 |
| 1. A method of managing a computer network, comprising: assigning a goal to a software, wherein the software agent has its own Agent Runtime Environment (ARE); is able to communicate with other software agents in the computer network; is capable of perceiving its own state; and is able to clone itself, and wherein the goal is a programmatic expression of a predefined task for the software agent; using a Transaction Processing Monitor for at least one of a fault-tolerant temporary storage and inter-ARE communication by the software agent across the computer network; creating test policy and modeling a behavior of the computer network based on the test policy to determine an optimal policy for the computer network, including predicting a failure of a network component based on a prediction algorithm; wherein said modeling comprises determining appropriate policy based on the prediction, and wherein the test policy is created by a modeler; providing a security service for authentication and authorization of intra-modeler and inter-modeler communication for preventing viral attacks on the computer network; and dynamically modifying the assigned goal of the software agent by replacing the assigned goal based on the optimal policy; wherein the software agent comprises an autonomous agent operable to request further policy when it lacks an ability to perform tile predefined task. |
1. 一種電腦網路管理方法,包括:指派一目標給一軟體,該軟體代理人具有自有之代理人執行環境、可與位於該電腦網路內的其他軟體代理人通訊、可查知自我狀態及可自行複製;該目標則為給予該軟體代理人之預先定義任務之程式化敘述;在至少一個容錯暫時儲存與互連軟體代理人經由電腦網路,在代理人執行環境間之通訊中,使用一交易處理監控程式;產生測試指令,並根據該測試指令建模該電腦網路之行為,以決定一個對該電腦網路之最佳化指令,包括以一預測演算法預測一網路組件之錯誤;該建模行為包括基於該預測決定適當的指令,而該測試指令由一模擬器產生;提供一安全服務予內部模擬器及互連模擬器間之通訊確認及授權,以避免該電腦網路之病毒攻擊;並基於該最佳指令,以置換該交付目標之方式動態修正交付該軟體代理人之目標;該軟體代理人具有一自動代理人,當其缺乏執行該被預訂任務之能力時,可要求更多指令。 |
表三、專利訴訟案件基本資料:NetFuel控告F5 Networks
| 訴訟名稱 |
NetFuel, Inc.v. F5 Networks, Inc. |
| 提告日期 |
2013年11月4日 |
| 原告 |
NetFuel, Inc. |
| 被告 |
F5 Networks, Inc. |
| 案號 |
1:13-cv-07895 |
| 訴訟法院 |
United States District Court, The Northern District of Illinois, Eastern Division |
| 系爭專利 |
US7,747,730、US8,131,851 |
| 系爭產品 |
BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM)、BIG-IP Global Traffic Manager (GTM)、BIG-IP Access Policy Manager (APM)、BIG-IP Advanced Firewall Manager (AFM)、BIG-IP Application Acceleration Manager (AAM)、BIG-IP Application Security Manager (ASM)、BIG-IP Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) 、BIG-IP Edge Gateway、Enterprise Manager、BIG-IP Link Controller以及BIG-IP Policy Enforcement Manager (PEM) |
| 訴狀下載 |
 |
Source: 科技政策研究與資訊中心 — 科技產業資訊室整理,2013/11
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------